Using DBIx::Class within a Dancer application
DBIx::Class, also known as DBIC, is one of the many Perl ORM
(Object Relational Mapper), but it's commonly recognised as the best
and most widely used.
This is a nice presentation from Leo : http://www.slideshare.net/ranguard/dbixclass-beginners-presentation
Basically, DBIC allows you to interact with your SQL Database without writing any SQL.
To do that, you need a set of Schema classes that describes your database structure. Then you can use DBIC to create, update, delete, search, and do many more things on the data that are in your database.
From a Dancer web application, it is very easy to use DBIC, thanks to
Dancer::Plugin::DBIC. This article will implement a simple web application to
demonstrate the use of Dancer::Plugin::DBIC.
Note : Although this article only skims the surface of DBIX::Class, it
won't explain how to use it. We recommend you to have a look at
DBIx::Class::Manual::Intro or DBIx::Class::Manual::Example if needed.
The bookstore example
Let's consider a simple Dancer application that allows to search for authors or books. The application is connected to a database, that contains authors, and their books. The website will have one single page with a form, that allows to query books or authors, and display the results.
To keep this article short, the HTML will be simplistic, and the implementation
as well. However, we'll try to explain how to properly use
Dancer::Plugin::DBIC.
The application will be structured as follow:
-
a Dancer route /search to handle the request, and decide if there is any search to perform, and send the results to the view
-
a view, that will display the search form, and the results if any.
-
a set of models, linked to a database, that will contain the books and authors. These models will be created using DBIC
The basics
Create the application
Okay, that's easy enough:
$> dancer -a bookstore
Change template type
We'll want to loop on results and display authors and books, and it's easier to
use Template Toolkit to do that, rather than the default
Dancer::Template::Simple.
So let's specify in the configuration that we'll use Template Toolkit as template engine:
# add in bookstore/config.yml template: template_toolkit
Create a view
We need a view to display the search form, and below, the results, if any. The
results will be fed by the route to the view as an arrayref of results.
Each result is a hashref, with a author key containing the name of the
author, and a books key containing an arrayref of strings : the books
names.
That explanation is probably hard to follow, so here is an example, much easier:
# example of a list of results
[ { author => 'author 1',
books => [ 'book 1', 'book 2' ],
},
{ author => 'author 2',
books => [ 'book 3', 'book 4' ],
}
]
So, what will the view look like? Here is a simple example, displaying the
search form, and the results, if any. It's written in Template Toolkit, but
Dancer changes the default [‰ %] format to be <% %> instead.
# bookstore/views/search.tt
<p>
<form action="/search">
Search query: <input type="text" name="query" />
</form>
</p>
<br>
<% IF query.length %>
<p>Search query was : <% query %>.</p>
<% IF results.size %>
Results:
<ul>
<% FOREACH result IN results %>
<li>Author: <% result.author.replace("((?i)$query)", '<b>$1</b>') %>
<ul>
<% FOREACH book IN result.books %>
<li><% book.replace("((?i)$query)", '<b>$1</b>') %>
<% END %>
</ul>
<% END %>
<% ELSE %>
No result
<% END %>
<% END %>
Create a route
Let's create a simple Dancer route, to be added in the bookstore.pm module:
# add in bookstore/lib/bookstore.pm
get '/search' => sub {
my $query = params->{query};
my @results = ();
if (length $query) {
@results = _perform_search($query);
}
template 'search', { query => $query,
results => \@results,
};
};
It's rather simple: get the parameter called query, if it exists perform the
search, and in any case, call the search view.
So, as you can see, we need to write the _perform_search() method. But
before we do that, let's create the database.
Create a database
We'll go with SQLite, as it fits well with the aim of simplicity of this example. Let's create the SQLite file database:
$> sqlite3 bookstore.db CREATE TABLE author( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT NULL, firstname text default '' not null, lastname text not null); CREATE TABLE book( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT NULL, author INTEGER REFERENCES author (id), title text default '' not null );
Simple stuff: we have 2 tables, one for authors, and one for books, that points to the author table.
Populate with some data
Let's write a script to populate the database with some data. We'll use
DBIX::Class, and let it discover our simple database schema.
# populate_database.pl
package My::Bookstore::Schema;
use base qw(DBIx::Class::Schema::Loader);
package main;
my $schema = My::Bookstore::Schema->connect('dbi:SQLite:dbname=bookstore.db');
$schema->populate('Author', [
[ 'firstname', 'lastname'],
[ 'Ian M.', 'Banks' ],
[ 'Richard', 'Matheson'],
[ 'Frank', 'Herbert' ],
]);
my @books_list = (
[ 'Consider Phlebas', 'Banks' ],
[ 'The Player of Games', 'Banks' ],
[ 'Use of Weapons', 'Banks' ],
[ 'Dune', 'Herbert' ],
[ 'Dune Messiah', 'Herbert' ],
[ 'Children of Dune', 'Herbert' ],
[ 'The Night Stalker', 'Matheson' ],
[ 'The Night Strangler', 'Matheson' ],
);
# transform author names into ids
$_->[1] = $schema->resultset('Author')->find({ lastname => $_->[1] })->id
foreach (@books_list);
$schema->populate('Book', [
[ 'title', 'author' ],
@books_list,
]);
Then run it in the directory where bookstore.db sits:
perl populate_database.db
And that's our database populated !
Use Dancer::Plugin::DBIC
Let's go back to our Dancer application now. Instead of interacting with the
database using SQL, let's configure DBIX::Class. DBIC needs to understand how
your data is organised in your database. There are two ways of letting DBIC
know:
-
either by writing a set of Perl modules, called schema modules: they will describe the database schema, each module describing one entity,
-
or by letting DBIC connect to the database, explore it, and generate the schema itself.
We'll demonstrate the use of the two solutions. The author of this article (dams) is not a big fan of the detection method: on complex database, it doesn't get everything right, so one needs to help DBIC. Describing the schema manually in proper Perl classes seems a cleaner option. But hey, TIMTOWTDI.
Use auto-detection
Let's add some configuration in our Dancer application. We want to indicate
that we want to use the Dancer::Plugin::DBIC plugin, and how we want to use
it. We also want to define a new DBIC schema, that we will call bookstore.
And we need to indicate that this schema is connected to the SQLite database we
created.
# add in bookstore/config.yml
plugins:
DBIC:
bookstore:
dsn: "dbi:SQLite:dbname=bookstore.db"
We could potentially define more schemas, by adding more fields under the DBIC: entry.
Note : you've noticed that we have only described which database to link the
schema to. That way, we let Dancer::Plugin::DBIC connect to the database and
discover its schema, and make it available for us
Now that the configuration is done, let's see what needs to be done in the code.
First of all, we need to indicate to Dancer that we want to use
Dancer::Plugin::DBIC. That's easily done:
# add in bookstore/lib/bookstore.pm use Dancer::Plugin::DBIC;
And now we can implement _perform_search using Dancer::Plugin::DBIC. The
plugin gives you access to an additional keyword called schema, which you give the
name of schema you want to retrieve. It returns a
DBIx::Class::Schema::Loader (because we let the plugin discover the schema
for us). This returned object can then be used to get a resultset and perform
searches, as per standard usage of DBIX::Class.
# add in bookstore/lib/bookstore.pm
sub _perform_search {
my ($query) = @_;
my $bookstore_schema = schema 'bookstore';
my @results;
# search in authors
my @authors = $bookstore_schema->resultset('Author')->search({
-or => [
firstname => { like => "%$query%" },
lastname => { like => "%$query%" },
]
});
push @results, map {
{ author => join(' ', $_->firstname, $_->lastname),
books => [],
}
} @authors;
my %book_results;
# search in books
my @books = $bookstore_schema->resultset('Book')->search({
title => { like => "%$query%" },
});
foreach my $book (@books) {
my $author_name = join(' ', $book->author->firstname, $book->author->lastname);
push @{$book_results{$author_name}}, $book->title;
}
push @results, map {
{ author => $_,
books => $book_results{$_},
}
} keys %book_results;
return @results;
}
We needed to do some data fiddling so that the books results are gathered by authors.
Use home-made schema classes
Writing your own DBIC schema classes goes a bit beyond this article, but here
are the basics. You can either have the .pm files be generated from you
using dbicdump (see DBIx::Class::Schema::Loader), and then you can modify
them to fit your needs. Or you can write them yourself from scratch, as
explained in the DBIC documentation.
A third option is to use the nice DBIx::Class::MooseColumns that let's you
write the DBIC schema classes using Moose. This way of doing make it look
more like ActiveRecord declarations.
You should put your schema classes in a place that Dancer will find. A good place is in bookstore/lib/.
Once your schema classes are in place, all you need to do is modify config.yml to specify that you want to use them, instead of the default auto-detection method:
# change in bookstore/config.yml
plugins:
DBIC:
bookstore:
schema_class: My::Bookstore::Schema
dsn: "dbi:SQLite:dbname=bookstore.db"
The rest will work exactly the same.
Start the application
Our bookstore lookup application can now be started using the built-in server:
# start the web application bookstore/bin/app.pl
Now if we search for The, here is what we get :
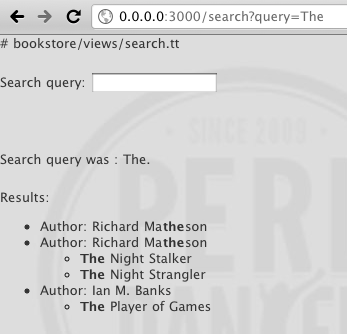
As you can see, the page presents 4 results. The first one is an author's match, Richard Matheson. The next 2 ones are 2 of his books. The last one is The Player of Games (a great book by the way...).
Conclusion
Well that was a rather long article, but we wanted to show a real example of
using DBIC in Dancer. Most of the Dancer Plugins have the same spirit in
common: be as simple as possible, and don't get in the way of the user.
Dancer::Plugin::DBIC is exactly that, and we hope we demonstrated it to you.
AUTHOR
dams ( Damien Krotkine <dams@cpan.org> )